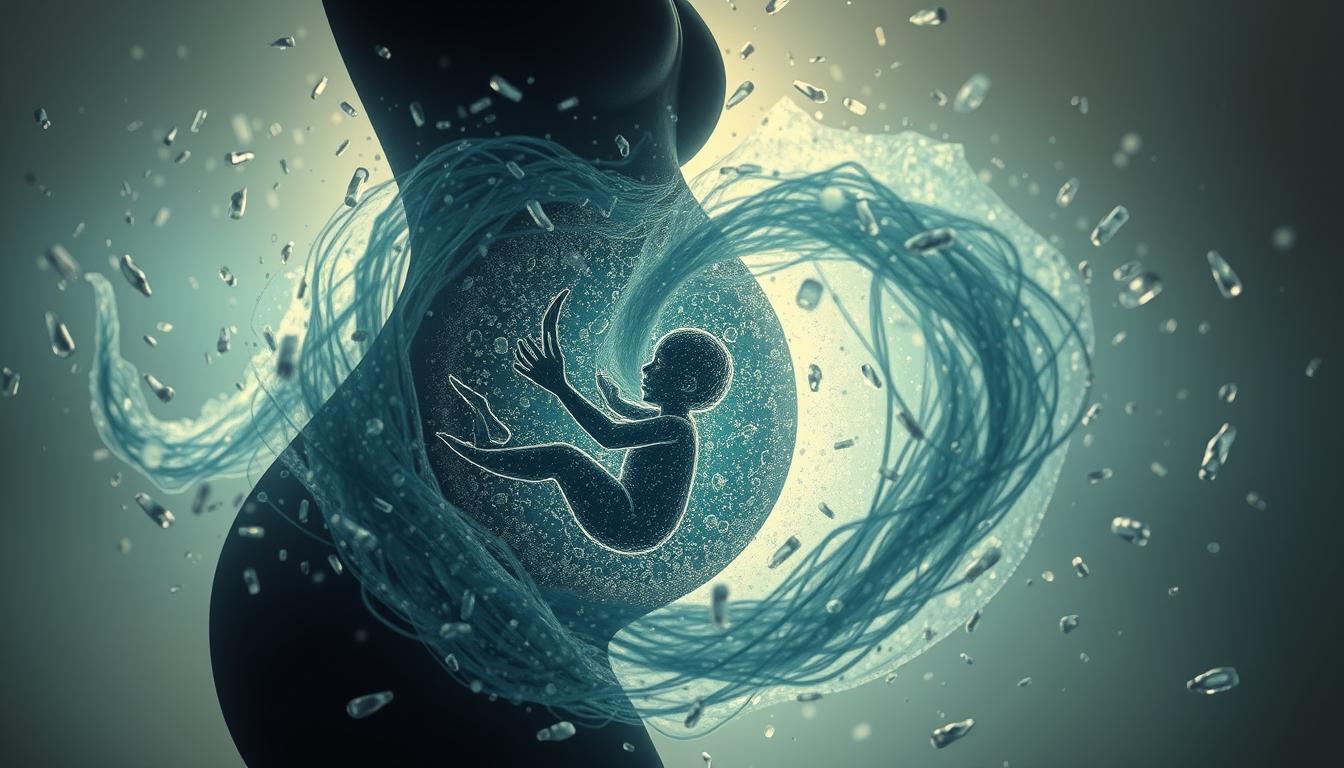
When you think about microplastic pollution and your health, it’s key to know about the gut microbiome. This part of your body is vital for your well-being. Microplastic pollution can harm this balance1.
The gut microbiota is mostly made up of bacteria from the Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes phyla. Other important bacteria include Actinobacteria and Proteobacteria1. You can lower your microplastic exposure to help your gut health. The Bye Microplastics AI mobile app can help, available on App Store and Google Play.
Microplastics have been found in human breast milk, worrying about their health effects on babies. This shows we need to tackle the issue of gut microbiome disruption from microplastics2. Studies say we might eat up to 5 grams of microplastics each week2.
This can make the Bacteroidetes phylum less common in our guts. This phylum has anti-inflammatory effects2
Understanding the Gut Microbiome
Research shows that the gut microbiome is key for our immune system, digestion, and mental health3. An imbalance, or dysbiosis, can cause health problems. Keeping our gut microbiome healthy is vital for our well-being. This can be done by understanding what affects the balance of our gut flora.
The gut microbiome is home to trillions of microorganisms. They are essential for our health. Diet, lifestyle, and exposure to pollutants like microplastics can affect this balance4. Knowing the importance of gut health helps us take steps to keep our microbiome balanced. This might involve using technology and making choices to reduce microplastic exposure.
Here are some important tips for a healthy gut microbiome:
- Be aware of microplastic exposure and try to reduce it
- Eat a balanced diet that supports gut health
- Stay updated on the latest gut health and microbiome research
By following these tips, we can support a healthy gut microbiome. This is important for a strong immune system and preventing diseases related to gut health3.
The Link Between Microplastics and Health
Microplastic pollution is a growing concern. It can harm human health5. These tiny plastic pieces are found in many products, like cosmetics and food packaging5. They can get into our bodies through eating, breathing, or skin contact, leading to health issues.
To lower our exposure, we need to know where microplastics come from. They can be in our food, clothes, and personal care items6. It’s important to be aware and take steps to reduce our contact with them.
Research shows microplastics can get into our cells and bloodstream, causing health problems5. Long-term exposure might lead to lung diseases like asthma6. The production of microplastics is expected to rise sharply, making action urgent6.
| Source | Microplastic Production | Health Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Link 1 | Estimated plastic consumption by individuals is around five grams per week5 | Microplastics can penetrate human cells and enter the bloodstream5 |
| Link 2 | Microplastics production worldwide is projected to increase by 155–265 million tons annually by 20606 | Long-term exposure to microplastics can result in lung diseases such as asthma and pneumoconiosis6 |
| Link 3 | Global production of plastics had increased to 359 million metric tons per year by 20187 | Microplastics have been found in various environments, including soil, air, and water7 |
Understanding the health risks of microplastics helps us take action5. We can choose products with less packaging, avoid microbeads, and support policies to reduce pollution6.
Microplastics Found in Human Breast Milk
Recent studies have found microplastics in human breast milk, which is worrying for infants’ health8. These microplastics could come from the mother’s exposure to them during pregnancy or while nursing. Microplastics are tiny pieces of plastic that break down from larger plastic items9.
This discovery calls for more research on how microplastics affect our health. A study found microplastics in 75% of breast milk samples10. On average, there were 1.1 microplastic particles per milliliter in breast milk10. This is concerning because it could harm the gut flora impact and lead to plastic particles in intestines due to microplastic pollution.
There’s a strong link between plastic pollution in the mother’s environment and microplastics in breast milk. When plastic pollution is higher, so is the chance of finding microplastics in breast milk, by 60%10. This means babies might swallow about 2,000 microplastic particles every day10.
| Study Findings | Percentage of Samples |
|---|---|
| Detection of microplastics in breast milk | 75% |
| Average concentration of microplastics | 1.1 microplastic particles per milliliter |
| Correlation between plastic pollution and microplastic detection | 60% increase |
Mechanisms of Microbiome Disruption
It’s key to know how microplastics mess with our gut microbiome to fight microplastic exposure. Studies show that microplastics can change the mix of bacteria in our gut11. This change can cause inflammation and make toxins, harming our health. The process is complex, involving our immune system and the production of harmful chemicals.
Microplastics can really mess with our gut microbiome, leading to gut microbiome disruption from microplastics. This messes with our microbiome balance and ups the risk of environmental contaminants. With plastic production hitting 320 million tonnes yearly11, and 8 million tonnes of plastic waste in the ocean annually11, we must tackle microplastic pollution.
To grasp how microplastics disrupt our microbiome, we must look at a few key points:
* How they change our gut’s bacterial balance
* The role of inflammation and toxins in this disruption
* The impact on our gut bacteria’s mix
* The health risks of microplastic exposure, including gut microbiome disruption from microplastics and microbiome balance disruption by environmental contaminants12.
By studying these aspects, researchers can better understand how microplastics disrupt our microbiome. They can then work on ways to lessen microplastic exposure and its health impacts11.
Symptoms of Gut Microbiome Disruption
It’s important to know the signs of gut microbiome disruption to get medical help and lower microplastic exposure. Symptoms can be different for everyone, but common ones include bloating, stomach pain, and changes in how often you go to the bathroom6. This disruption can also weaken your immune system, making you more likely to get sick13.
Some key symptoms of gut microbiome disruption are:
- Digestive issues, such as bloating and abdominal pain
- Changes in bowel movements
- Increased susceptibility to infections
These signs can happen because of changes in the bacteria in your gut. This can be caused by eating plastic and being exposed to harmful substances in the environment12.
Knowing these symptoms and trying to avoid microplastics is key to keeping your gut healthy. By understanding how microplastics affect your gut, you can take steps to protect your health and lower the risk of long-term diseases13.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Digestive issues | Bloating, abdominal pain, changes in bowel movements |
| Immune function | Increased susceptibility to infections |
By spotting the signs of gut microbiome disruption and cutting down on microplastic exposure, you can keep your gut healthy. This helps prevent long-term diseases6.
Long-term Health Consequences
It’s important to understand how microplastics affect our health over time. Studies show they might be connected to diseases like obesity, diabetes, and heart disease14. We need more research to know how this happens.
Reducing microplastic pollution is key to preventing these diseases. Microplastics can disrupt our gut health, leading to digestive issues and weakened immunity14. This imbalance can cause many health problems.
Microplastics in our food and drinks can harm our health. They can build up in our guts, causing problems with digestion and increasing the risk of stomach issues14. This is why we must be careful about what we eat and drink.

To fight microplastic pollution, we must reduce our exposure. We can do this by using fewer single-use plastics, recycling, and supporting policies against microplastic pollution7. By doing these things, we can protect our health and the planet.
Preventing Microplastics Exposure
To fight microplastic pollution’s impact on gut health, we must cut down on microplastic use. It’s key to adopt safe habits15. We can do this by picking products with less packaging and steering clear of microbeads13. These actions help us fight pollution and keep our environment healthy.
Here are some tips to cut down on microplastic use:
- Choose products with minimal packaging
- Stay away from products with microbeads
- Opt for clothes made from natural fibers
Practicing safe disposal of plastic waste is also vital15. Being careful about what we use and throw away helps reduce pollution. This, in turn, supports better gut health.
Studies show microplastics are everywhere, from oceans to rivers and even in our water13. By lowering our exposure, we can lessen their damage to our health and the planet.
Probiotics and Their Role in Gut Restoration
Probiotics are live microorganisms that help restore the gut microbiome balance. This balance can be disrupted by microplastics16. You can find them in foods like yogurt and kefir or take them as supplements. Using probiotics can lessen the harm from microplastics and keep your microbiome healthy.
Probiotics are known to improve digestion, boost the immune system, and lower inflammation17. They help balance the gut bacteria, which is key for a healthy gut. Look for strains like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium in fermented foods or supplements.
Adding probiotics to your diet supports your gut’s health and reduces microplastic harm. This can improve your overall health and wellbeing. It also helps maintain a healthy microbiome balance16.
Remember, probiotics are just one part of the solution. They should be used with other methods to cut down on microplastic exposure. This includes using less plastic and recycling more17. A holistic approach to gut health can help counteract microplastic effects and support a healthy gut flora impact.
Future Directions in Research
Research on microplastic pollution and its health effects is growing. We need to look into new areas of study. Studies on microplastics and microbiomes are showing how they affect our health18. For example, microplastics can lower the good bacteria in our bodies, which helps fight inflammation18.
We also need better policies to tackle microplastic pollution. This could mean banning microbeads in cosmetics or using biodegradable plastics. Recent studies found microplastics in human stool, mostly in people with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)19.
Some important research areas include:
- Studying how microplastics affect our gut and increase disease risk
- Finding ways to cut down on microplastic pollution and support green practices
- Looking into how environmental pollutants mix with microplastics and harm our health18
By diving deeper into the links between microplastics, environmental pollutants, and gut health, we can improve our environment. This will help reduce the dangers of microplastic exposure19.
| Microplastic Type | Detection Rate |
|---|---|
| Polypropylene (PP) | 62.8% |
| Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) | 17.0% |
Conclusion: The Importance of Awareness
Call to Action for Public Health
We all must do our part to cut down on plastic use and push for better policies against microplastic pollution20. By choosing to use less plastic, recycling well, and pushing for stronger rules, we help our planet and our health. This protects our gut microbiome too.
Encouraging Sustainable Practices
Adopting green habits at home and in our communities makes a big difference4. Using eco-friendly products, backing companies that handle plastic wisely, and teaching others about reducing microplastics are key. Together, we can make our future cleaner and greener.
FAQ
What is the gut microbiome and why is it important for overall wellness?
How can microplastics disrupt the gut microbiome?
What are the sources and pathways of microplastic exposure?
What are the implications of detecting microplastics in human breast milk?
What are the symptoms of gut microbiome disruption caused by microplastics?
What are the potentially long-term health consequences of microplastic exposure?
How can individuals reduce their exposure to microplastics?
How can probiotics help restore a healthy gut microbiome?
What are the future directions in research on microplastics and microbiomes?
Source Links
- Microplastics and microbiota: Unraveling the hidden environmental challenge
- Mind over Microplastics: Exploring Microplastic-Induced Gut Disruption and Gut-Brain-Axis Consequences
- The impact of microplastics on the gut microbiome and health
- PET microplastics affect human gut microbiota communities during simulated gastrointestinal digestion, first evidence of plausible polymer biodegradation during human digestion – Scientific Reports
- How do microplastics impact our gut health?
- Frontiers | Effect of microplastics on nasal and intestinal microbiota of the high-exposure population
- Immunotoxicity and intestinal effects of nano- and microplastics: a review of the literature – Particle and Fibre Toxicology
- Detection of Microplastics in Human Breast Milk and Its Association with Changes in Human Milk Bacterial Microbiota
- Microplastics Everywhere
- Microplastics are in our bodies. Here’s why we don’t know the health risks
- Microplastics and human health: unveiling the gut microbiome disruption and chronic disease risks
- Plastics and the microbiome: impacts and solutions – Environmental Microbiome
- Microplastics and human health: unveiling the gut microbiome disruption and chronic disease risks
- How microplastics affect gut health
- Frontiers | Microplastics and human health: unveiling the gut microbiome disruption and chronic disease risks
- Could probiotics protect against human toxicity caused by polystyrene nanoplastics and microplastics?
- Probiotics an emerging therapeutic approach towards gut-brain-axis oriented chronic health issues induced by microplastics: A comprehensive review
- Mind over Microplastics: Exploring Microplastic-Induced Gut Disruption and Gut-Brain-Axis Consequences
- Microplastics: an often-overlooked issue in the transition from chronic inflammation to cancer – Journal of Translational Medicine
- Effects of Microplastic on Human Gut Microbiome: Detection of Plastic-Degrading Genes in Human Gut Exposed to Microplastics—Preliminary Study